- The WhatsUp Gold’s free Syslog Server is a feature-rich tool that addresses most administrators syslog needs. The toll has enhanced export capabilities and can display logged messages in real-time, optionally filtering results to customize the display to one’s specific needs.
- Kiwi Syslog Server Free Edition by SolarWinds (FREE DOWNLOAD) Kiwi Syslog Server.
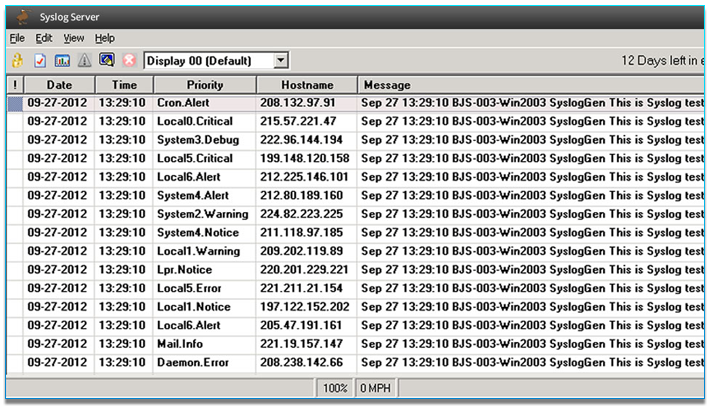
SolarWinds Kiwi Syslog Server. Kiwi is a SolarWinds product, so you know it is good.
By default, Apache stores all logs to the local disk. This works well for development environments and small deployments, but becomes unsustainable once you have more than one server. Not only is it frustrating having to open each log file on each server, but trying to trace requests across multiple servers can quickly become time-consuming.
Log centralization services prevent this by allowing you to store logs from your Apache servers in a single location. This makes it possible to view all of your web logs without having to open each log file individually. Many log centralization services can also automatically parse your logs, and provide a user interface that lets you scroll, search, and filter through your log data in near real time.
This section shows different methods of aggregating and centralizing logs from your Apache servers.
Syslog
Syslog is a logging service commonly found on Linux, Unix, and Mac systems. Syslog handles logs from a number of different sources including applications, system services, daemons, and hardware. Syslog is reliable, standardized, and can even forward your logs to another syslog server.
A common approach to reading Apache logs is to configure syslog with file monitoring. With file monitoring enabled, syslog periodically scans a file on the system for changes, then imports those changes into its own log file. The benefit is you get the complete original log message wrapped in the standard syslog message format without modifying the original file.
Configuring File Monitoring in Syslog
The most common way to enable file monitoring is by installing and configuring rsyslog. rsyslog is a complete syslog server with file monitoring built in. It’s easy to configure, fast, and supports log rotation, which is commonly found in Linux distributions such as Ubuntu.

The following rsyslog configuration monitors both the Apache access and error logs. You may need to replace the file names depending on your configuration.
Save this to your rsyslog configuration file, then restart the rsyslog service.
Some vendors have scripts or agents that will configure rsyslog to monitor these log files, making setup easier. For example, SolarWinds® Loggly® built a script that will automatically configure rsyslog to monitor your Apache logs.

Filtering Logs Before Centralization
In some situations, you may want to filter your logs before sending them to your centralization service. For example, you may only want to send error codes in order to use less storage on the remote system. With rsyslog, we can add a condition to our file monitoring rule that only allows events containing certain HTTP status codes.
This configuration example drops all messages where the status code is not 500 or 502. stop tells rsyslog to discard the message.
Piping to Logger
Apache doesn’t just support logging to files. For example, you can also send logs directly to a syslog service using a custom logging pipeline. The most common method is to use the /usr/bin/logger command, which forwards logs over a syslog socket to the syslog service. This lets you bypass the file monitoring process, which could have performance advantages on slower storage devices. In addition, you no longer have to store a separate log file for Apache.
The downside to this approach is it removes the local backup provided by your Apache logs. If there’s a problem sending your logs from logger to syslog, you could lose messages. In addition, logger supports a maximum message size of 1024 bytes. However, you can increase the size of this by adding the --size parameter.
To set up a logging pipe, open your Apache configuration file and replace your logging configuration with the following.
Restart the Apache service to apply the changes.
Mac Free Downloads
Now your logs will no longer be written to the access.log and error.log files, but will instead go straight to syslog. If you want to continue logging to file as well as syslog, you can use the following configuration instead. This uses the tee command to first pipe the log message to file, then pipes the output from that command to logger:
See it. Analyze it. Inspect it. Solve it
See what matters.
Mac Free Antivirus Download
START FREE TRIALSYSLOG SERVER/ANALYSIS
In a word: Splunk
it may be overkill, and it takes a little configuration to get going, but it does near-real time analysis and reporting any any number of log files from any number of systems. It's free for small volume (up to 500MB per day), but can run into some serious $$ if you're dealing with lots of logs (e.g. hundreds of GB per day)
LOAD TESTING A WEBSITE?:
There are sites that can do this, but I wouldn't worry about it. Your server is not going to be your limit, it's far more likely to be your network bandwidth. Any Mac Mini is more than capable of saturating most internet links, unless you're in a commercial datacenter with gigabit uplinks to your upstream providers.
I know there is a Mac OS X app that can test and map ones network, complete with graphical maps showing where each machine and server is located in the building
I'm not aware of any app that can build a physical map of your network, since that requires an understanding of building layouts, etc., but logical maps (a list of all the devices on the network, switch ports, etc.) are easy enough. Intermapper is probably a good starting point.
Syslog Server Mac Free Trial
Jan 26, 2011 10:14 AM